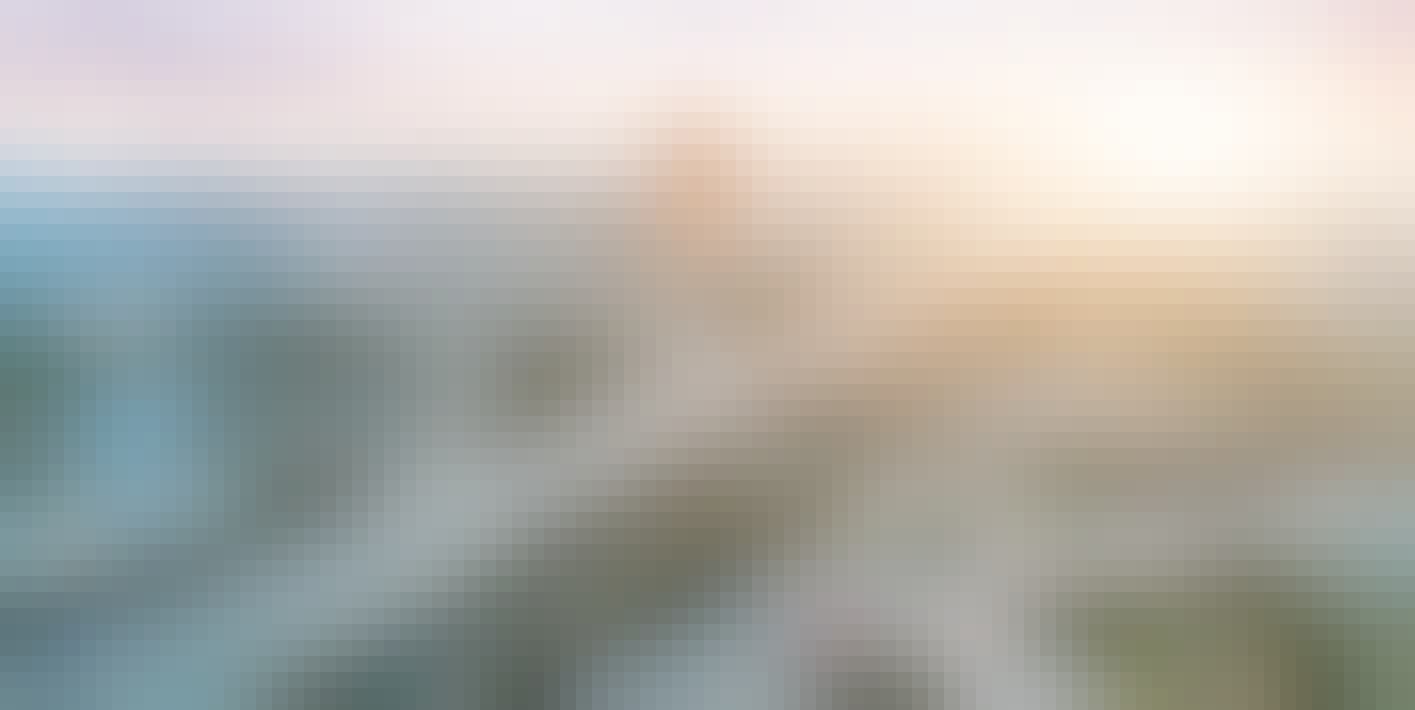
Joining a radome to the radar housing using the heat staking processes BHS HOT STAMP®
For the joining of a radome to the radar housing, a customer opted for heat staking processes instead of an originally envisaged bolting process in order to meet today's requirements for technical cleanliness and to save running costs. In designing the riveted joint, the customer followed the bdtronic design guideline.
The heat staking as the last manufacturing step is carried out via four riveting points in the product corners, whereby the free area around the riveting points for forming the rivet heads and supporting the tools is very tight. Joining of the radome to the housing as a "sandwich" structure takes place after metering of the liquid seal, which may be exposed to a maximum temperature of 80°C during the curing time of approx. 24 hours.
The BHS HOT STAMP® heat staking processes were chosen because they generate a very low temperature input on the component and the tools have the smallest diameters. The process simulation in the in-house technology center with subsequent service life tests in accordance with relevant standards by the customer showed that all requirements were met. The pin material selected is a special, durable semi-crystalline thermoplastic.
In the production flow, the assembly was transported into the hot riveting machine in such a way that the riveting pins were on the underside of the assembly, so that riveting against the direction of gravity was desired in order to dispense with turning the assembly before riveting. Turning the assembly after dispensing the sealant and bringing the entire assembly together is risky, as doing so could possibly negatively affect the cross-linking and bonding of the sealant.
BHS HOT STAMP® enables this process direction, which reduces the investment costs of the machine and allows the production sequence to be reproduced safely. A special punch was designed for the series production line which can be guided through the hold-down mask. Diverse product variants, some with different material types, are produced in a large number of production lines worldwide with a cycle time of 15 seconds.